Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Igawa, Naoki; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Shimura, Kenichiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 242(1-2), p.469 - 472, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)SiC/SiC composites are one of the candidate materials for first wall in a fusion reactor because of their high strength at high temperature and low residual radioactivity after irradiation. In the fusion reactor, these materials are required to have high thermal diffusivity for heat exchange and reducing the thermal shock. Under fusion conditions, helium (He) and hydrogen (H) are produced in SiC. In this study, the effect of He ions implantation on the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composite were investigated. In the results, the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composites decreased after He ions implantation. However, the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composites hardly reduced in the operation temperature of fusion reactor. The thermal diffusivities of He implanted specimens were partly recovered by annealing. The defect concentration induced by He implantation, X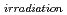 , in SiC/SiC composites was estimated. The X
, in SiC/SiC composites was estimated. The X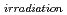 rapidly decreased around 500
rapidly decreased around 500  C. The reason is that the He release from SiC starts at 500
C. The reason is that the He release from SiC starts at 500  C.
C.
Baba, Shinichi; Nemoto, Makoto*; Sozawa, Shizuo; Yamaji, Masatoshi*; Ishihara, Masahiro; Sawa, Kazuhiro
JAERI-Tech 2005-055, 157 Pages, 2005/09
The Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) has been carrying out the research on radiation damage mechanism of heat-resistant ceramics composite materials, as one of the subjects of the innovative basic research on high temperature engineering using the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). A series of preliminary irradiation tests is being made using the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). The present report describes results of post-irradiation examinations so far on specimens irradiated in the second and third capsule, designated 98M-41A and 99M-30A, to fast neutron fluences of 1.0 10
10 m
m (E
(E 1MeV) at temperatures of 973K-1173K and 1273K-1473K. The PIE were conducted as the fundamental statistics index of the diametral dimensions for irradiated specimen, irradiation induced dimensional change rate and thermal expansion rate.
1MeV) at temperatures of 973K-1173K and 1273K-1473K. The PIE were conducted as the fundamental statistics index of the diametral dimensions for irradiated specimen, irradiation induced dimensional change rate and thermal expansion rate.
Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Igawa, Naoki; Miwa, Shuhei*; Wakai, Eiichi; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Snead, L. L.*; Hasegawa, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 335(3), p.508 - 514, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:89.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The microstructure of near-stoichiometric fiber SiC/SiC composites implanted with He and H ions was studied at implantation temperatures of 1000 and 1300  C. The average size of He bubbles in the CVI SiC matrix decreases with increasing concentration of implanted H ions. Moreover, the number density of He bubbles increases with increasing irradiation temperature and amount of implanted H. At the irradiation temperature of 1000
C. The average size of He bubbles in the CVI SiC matrix decreases with increasing concentration of implanted H ions. Moreover, the number density of He bubbles increases with increasing irradiation temperature and amount of implanted H. At the irradiation temperature of 1000  C, He bubbles were mainly formed at grain boundary within the matrix. On the other hand, He bubbles were formed both at grain boundaries and within grains at the irradiation temperature of 1300
C, He bubbles were mainly formed at grain boundary within the matrix. On the other hand, He bubbles were formed both at grain boundaries and within grains at the irradiation temperature of 1300  C. The average size of He bubbles at grain boundaries was much larger than within the grain. The average size of He bubbles in the fiber was smaller than that in the matrix in all cases.
C. The average size of He bubbles at grain boundaries was much larger than within the grain. The average size of He bubbles in the fiber was smaller than that in the matrix in all cases.
Nishio, Satoshi
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(1), p.14 - 17, 2004/01
SiC/SiC composite is a promising structural material candidate for fusion power cores and has been considered internationally in several power plant studies. It offers safety advantages arising from its low induced radioactivity and afterheat, and the possibility of high efficiency of energy conversion through high temperature operation. The latest SiC/SiC-based power core design studies are summarized, and the key SiC/SiC parameters affecting the performance of power core components are highlighted.
Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Igawa, Naoki; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Nozawa, Takashi*; Kato, Yudai*; Koyama, Akira*; Snead, L. L.*; McLaughlin, J. C.*
Advanced SiC/SiC Ceramic Composites: Developments and Applications in Energy Systems; Ceramic Transactions Vol. 144, p.69 - 76, 2002/00
Process optimization for Forced-thermal gradient Chemical Vapor Infiltration (FCVI) fabrication of 75 mm diameter size SiC composites with advanced SiC fibers; Hi-Nicalon Type S and Tyranno SA, was carried out. The SiC/SiC composites fabricated by FCVI exhibited significant reduction in porosity (15.1%) and more uniform pore distribution by decreasing the MTS and H gases flow rates in the latter part of the FCVI process. The tensile strength of the both composites using Hi-Nicalon Type S or Tyranno SA fibers was slightly increased with increased thickness of carbon interphase in the range of 75-300 nm. In order to perform the comparative testing required to directly compare the thermomechanical property changes following neutron irradiation, larger composites with uniform microstructural property are required. From the results of process optimization for fabrication of 75 mm diameter size FCVI SiC/SiC composites, the definitive purpose in this study is the fabrication of the 300 mm diameter size SiC/SiC composite with the uniform microstructural properties.
gases flow rates in the latter part of the FCVI process. The tensile strength of the both composites using Hi-Nicalon Type S or Tyranno SA fibers was slightly increased with increased thickness of carbon interphase in the range of 75-300 nm. In order to perform the comparative testing required to directly compare the thermomechanical property changes following neutron irradiation, larger composites with uniform microstructural property are required. From the results of process optimization for fabrication of 75 mm diameter size FCVI SiC/SiC composites, the definitive purpose in this study is the fabrication of the 300 mm diameter size SiC/SiC composite with the uniform microstructural properties.
Kurihara, Ryoichi; Nishio, Satoshi; Konishi, Satoshi
Thermal Stresses 2001, p.81 - 84, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Ozawa, Kazumi; Nozawa, Takashi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ioka, Ikuo; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kawanishi, Tomohiro; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Fukahori, Tokio; Nozawa, Takashi*; Watanabe, Seiichi*; Murakami, Nozomu*; Sato, Hisaki*; et al.
no journal, ,